Here, Andreas built and analysed several timelines along the first year of life of different mouse models to understand how pancreatic endocrine islets are maturing and then age. By combining transgenic systems, global transcriptomics, pathway analysis, cell biology and physiology, we mapped the age- specific cellular and molecular changes characterizing the gradual transition from young to seniority and identified a novel master regulator of pancreatic islet ageing modulating a critical subset of these processes. We showed that:
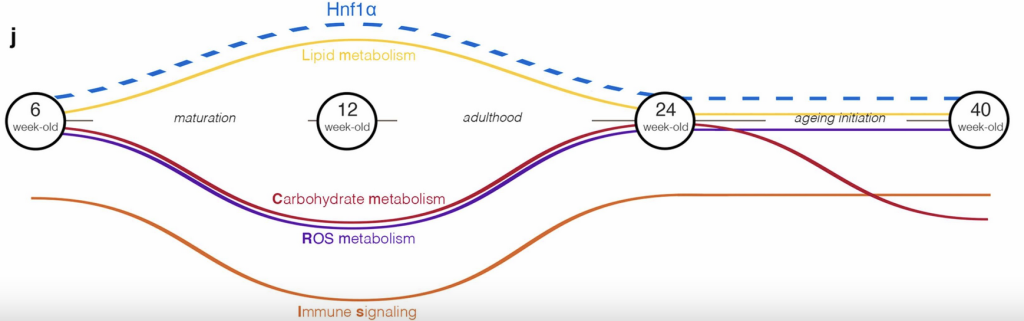
- Pancreatic islet maturation and ageing is controlled by a complex regulatory landscape as revealed by morphometry, physiology, and pathway analysis.
- Hnf1a is a novel master regulator of the maturation and ageing in the adult murine pancreatic islet during the first year of life.
- Suboptimal levels of HNF1A in the pancreatic islets disrupt normal ageing being characterized by molecular signatures mirroring premature metabolic maturation.
- The immune signaling activity pattern invariably opposed the one of Hnf1a, suggesting a regulatory relationship between the two.
- Age-specific regulation of Hnf1a is lost in immunodeficient mice
- The global proteome analysis of human islets spanning three decades of life revealed similarities in the age-specific regulatory landscapes and metabolic processes between mice and human
Continue your reading here:
Authors:
Mechanisms of Ageing and Development 2024 (in press) Volume 220, August 2024, 111951
DOI information: 10.1016/j.mad.2024.111951

1 comment for “Research Paper: The age-dependent regulation of pancreatic islet landscape is fueled by a HNF1a-immune signaling loop”