Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is the most common myeloid cancer in adults, arising from hematopoietic stem cells and marked by a rapid proliferation of immature myeloblasts. Its genetic and clinical diversity complicates treatment. Key mutated genes include NPM1, RUNX1, TP53, IDH1/2, and FLT3, the latter of which is altered in about one-third of AML cases. The FLT3-ITD mutation, a common and aggressive subtype, is strongly associated with poor clinical outcomes, highlighting an urgent need for targeted therapies.
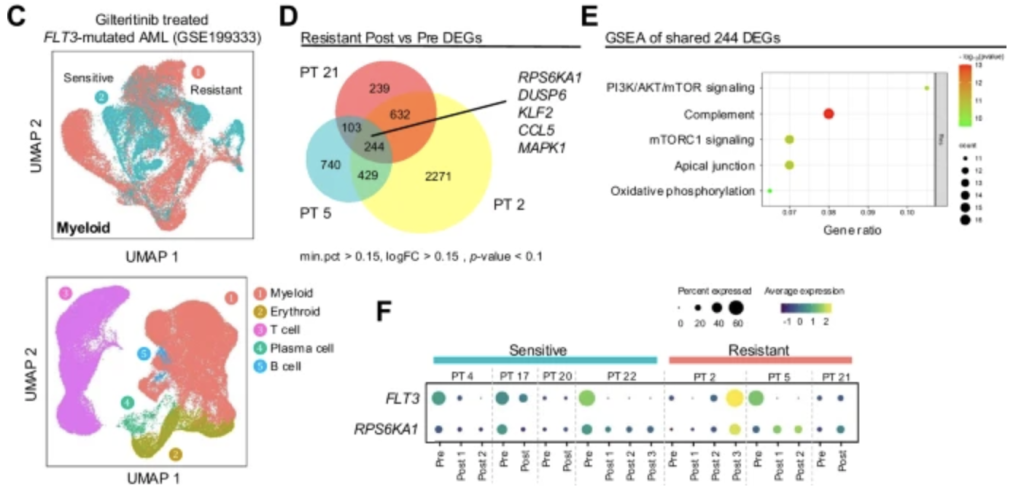
RSK1 (RPS6KA1) plays a critical role in regulating FLT3 activity in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), especially in cases with FLT3 mutations such as FLT3-ITD and FLT3 D835Y. A recent study published in the Journal of Blood Cancer on November 26, 2024 revealed that these mutations lead to elevated RSK1 phosphorylation and activation of downstream signaling pathways like S6. Analysis of AML patient data showed that FLT3 inhibitor-resistant patients had increased RPS6KA1 expression, suggesting that RSK1 is involved in treatment resistance.
Further research identified FLT3 and FLT3LG as co-dependences with RPS6KA1 in AML cells. FLT3 inhibitors like Quizartinib and Midostaurin suppressed RSK1 phosphorylation, confirming its role downstream of FLT3. Knockdown of RPS6KA1 induced apoptosis in FLT3-ITD AML cells, supporting RSK1 as a therapeutic target. The novel RSK1 inhibitor PMD-026 showed preferential sensitivity in FLT3-ITD cells, inhibiting RSK1 and disrupting cell cycle progression.
In vivo, PMD-026 reduced leukemic cells, extended survival, and suppressed leukemia hallmarks in mouse models. The treatment also led to decreased FLT3 protein expression, suggesting RSK1 regulates FLT3 stability through USP1. Inhibition of RSK1 increased FLT3 ubiquitination and degradation, a process mimicked by USP1 inhibition.
Clinical data from AML patients indicated that high USP1 expression correlates with poor survival, and elevated RPS6KA1 and USP1 were significant predictors of poor prognosis. These findings support RSK1 and USP1 as potential biomarkers for AML treatment and progression.
Continue your reading here:
Kong T, Laranjeira ABA, Letson CT, Yu L, He F, Jayanthan A, Los G, Dunn SE, Challen GA, Oh ST. RSK1 dependency in FLT3-ITD acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Cancer J. 2024 Nov 26;14(1):207. doi: 10.1038/s41408-024-01187-4.