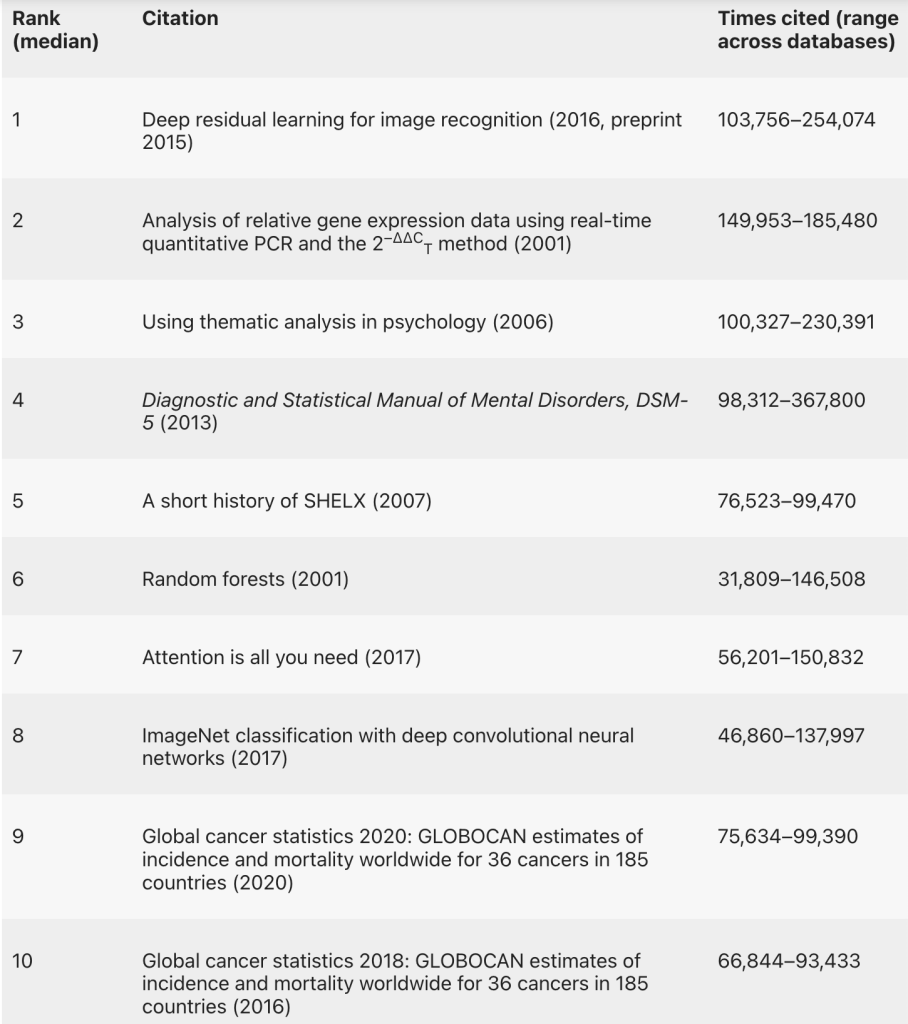
Today, Nature published a new feature examining the most cited papers of the twenty-first century (Pearson et al., 2025). The most cited paper is naturally connected to the neural-inspired algorithms that laid the foundation for deep learning and the AI we have come to both love and hate over the past year. However, this is not the paper I will focus on. Instead, I will discuss the second most cited paper. It might not have had an obvious high impact on science and the world, but it was created to simply give scientists something to cite.
According to Google Scholar, it has been cited a total of 188,579 times since its publication in 2001. This paper, authored by Livak and Schmittgen and published in Methods (Livak and Schmittgen, 2001), describes the use of the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method to analyze relative gene expression from quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) data. This method is mainly used to assess how gene expression changes between different treatments, such as drug treatment versus vehicle, gene silencing, etc. The equation was originally published in a manual for analyzing qPCR data, which was freely available. However, since citing a manual was not widely accepted in publications, Schmittgen contacted the original creator of the equation, Livak, and they published the paper. This allowed everyone performing qPCR analysis to cite a paper justifying their choice of calculation.
This feature and the paper in Methods show that while groundbreaking work gets highly cited, so does the work that everyone needs for their daily tasks. We look forward to all the great publications to come.
Continue your reading here:
- Pearson H, Ledford H, Hutson M, Van Noorden R. THE MOST-CITED PAPERS OF THE TWENTY-FIRST CENTURY. Nature. 2025. April;640: 588-592. doi: 10.1038/d41586-025-01125-9
- Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001 Dec;25(4):402-8. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262