Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is an aggressive blood cancer marked by the rapid expansion of immature myeloblasts. Despite progress in targeted therapies, resistance remains a major obstacle, especially in patients with mutations that impact the MAPK and apoptotic pathways. The anti-apoptotic protein BCL2 is often overexpressed in leukemia stem/progenitor cells, making it a prime therapeutic target. However, resistance to the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax frequently arises due to the stabilization of MCL1 via MAPK signaling, highlighting the need for combination therapies to improve treatment outcomes.
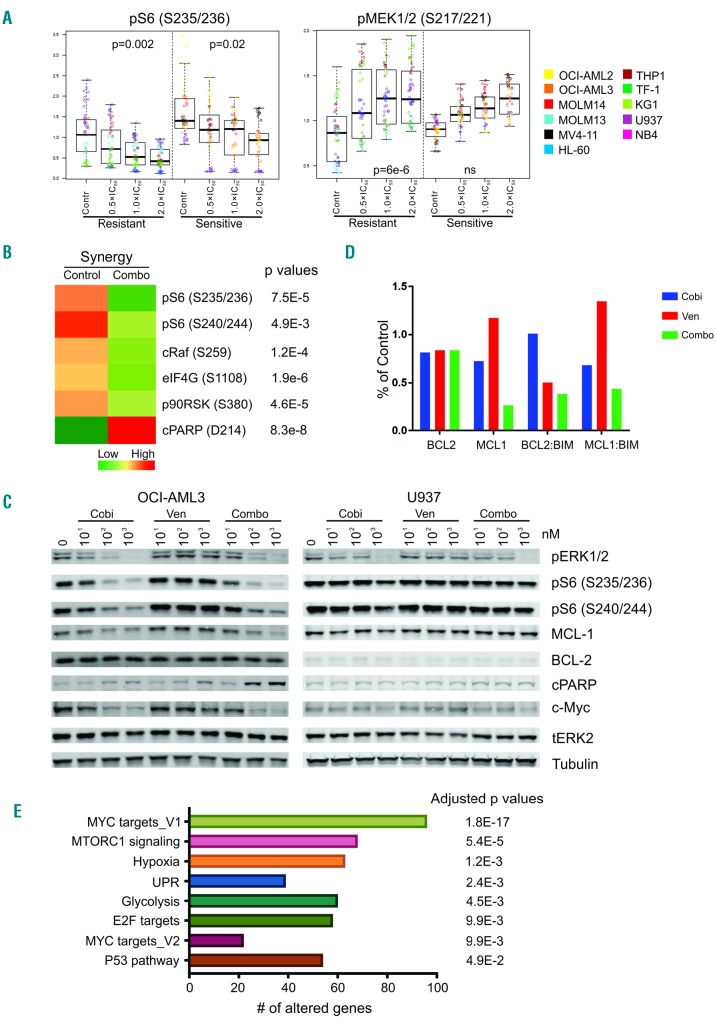
A recent study published in Haematologica demonstrated that combining BCL2 and MAPK pathway inhibition—using venetoclax alongside the MEK inhibitor cobimetinib—produced synergistic anti-leukemia effects in AML models. While venetoclax alone induced apoptosis in certain AML cells, cobimetinib prevented MCL1 stabilization by blocking MAPK signaling. CyTOF analysis revealed that BCL2 is highly expressed in leukemia stem/progenitor cells, especially in venetoclax-sensitive AML cases. Additionally, cobimetinib effectively suppressed key survival signals like pERK and pS6 in AML.
Proteomic and transcriptomic analyses identified downregulation of MYC, mTORC1, and p53 pathways as crucial factors in the combination’s effectiveness. In AML cell lines, cobimetinib reduced MCL1 levels and disrupted complexes between BCL2:BIM and MCL1:BIM, freeing BIM to promote apoptosis. This combination showed synergy in 7 out of 11 AML cell lines, even those resistant to single-agent treatments. In primary AML patient samples, the combination inhibited leukemia progenitor function while leaving normal hematopoietic progenitors unharmed, emphasizing its potential for therapy.
In vivo, the combination of venetoclax and cobimetinib significantly reduced leukemia burden in xenograft AML models. Mice treated with the combination exhibited lower tumor burden and extended survival compared to controls. However, complete remission was not achieved, likely due to the protective role of the bone marrow microenvironment.
Continue your reading here:
Han L, Zhang Q, Dail M, Shi C, Cavazos A, Ruvolo VR, Zhao Y, Kim E, Rahmani M, Mak DH, Jin SS, Chen J, Phillips DC, Koller PB, Jacamo R, Burks JK, DiNardo C, Daver N, Jabbour E, Wang J, Kantarjian HM, Andreeff M, Grant S, Leverson JD, Sampath D, Konopleva M. Concomitant targeting of BCL2 with venetoclax and MAPK signaling with cobimetinib in acute myeloid leukemia models. Haematologica 2020 Mar;105(3):697-707 doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.205534. PMID: 31123034 doi:10.3324/haematol.2018.205534